VPS vs VPN – While they might sound the same, it is necessary to consider the difference between VPS vs VPN. They both(VPS vs VPN) have the word “virtual in their names, but there is not so much common in them.
VPS is a dedicated OS hosted offline. It is offered as a service. At the same time, VPN is a network of dedicated servers that facilitate the use of the internet. A VPS is a computer, and a VPN is a service. VPS vs VPN.
Table of Contents
Before going for VPS vs VPN, let you know
What is a VPS?
VPS, or a virtual private server, is a server divided into several smaller ones. VPS is most commonly used for web hosting, allowing you to host your site on a virtual server environment. A server is like the home for all the data and files your website has.
It is private because the server is reserved for you. And it’s virtual since VPS technology uses a parent server to host multiple virtual servers that work as separate entities. So, users don’t need to share RAM or storage space. That said, we can think of a VPS as one big computer, running lots of little computers inside of it.

VPS is typically used for smaller workloads that require consistent performance. Here’s when businesses may use this solution:
- Hosting 1-10 websites with high traffic
- A website exceeds the limits of its shared hosting
- Root access to the server is required
- Scalability is needed as the business grows
Pros of VPS
- High Scalability
- Complete Customization
- Affordable than a Dedicated Server
- High-Performance
Cons of VPS
- Pricier than Shared Hosting
- Less flexible than Dedicated Server
- Requires good Technical Knowledge.
What is VPS used for?
VPSs are most commonly used for website hosting. Usually, you’d want one when you need anything hosted on a server.
Here are a few scenarios where you might want to use a virtual private server:
- You are running a powerful application that requires a lot of CPU;
- You host a high-traffic website and need more resources for better performance;
- You are hosting a website with an eCommerce platform and need it to run smoothly;
- You need to run applications or software remotely;
- You need scalability as your business grows.
If you find yourself in any of these situations, VPS will come in handy for you, but are there any more reasons to consider it?
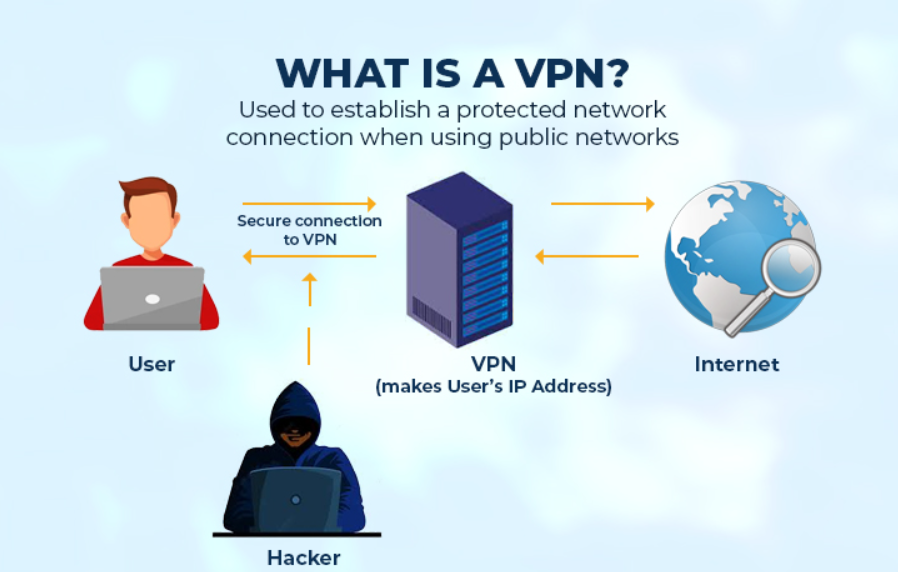
What is a VPN?
VPN means Virtual Private Network and is a private way of relating through the internet from point to point. A VPN allows users in one location to enter an encrypted “tunnel” at their end and exit the tunnel at some other point.
For some, a VPN is a way around local censorship, permitting a user to enter the tunnel in a country with strong government controls around internet usage and leave the tunnel in another country with more space for use. For others, it’s a way of linking from their home to their work without anyone in between capable of monitoring the documents, media, email, files, or other use, delivering them a secure way of working remotely. What does ovh stand for VPN? OVH stands for Online Virtual Hosting.
Pros of VPN
- Access geo-locked content
- Hide your private information
- Provide safety through anonymity
- Secure connection for remote work
Cons of VPN
- Slowness in connection speed
- Complicated configuration
- Less security with free or low-quality VPNs
How Does a VPN Work?
VPN providers have dozens, hundreds, or even thousands of servers often spread worldwide. When you download the VPN software onto your computer, mobile device, or router, it confirms that your
internet traffic goes to one of these servers before getting the website or the application you’re using. It hides your actual IP address and makes it look like your internet traffic is coming from the VPN’s server. It can modify your apparent location to another city or even another country. To “tunnel” your data and separate it from other data traveling online, VPN providers “encapsulate” it. It puts a digital wrapping of other data around it, making it hard to tell what it is.
As we explained above, VPN providers also encrypt your data, making it even harder to hack. Encryption translates your data into a complex code that you can only read with the right decoding tool. It means that even if a cybercriminal or spy worked to find your data in a tunnel, they would have to crack its code to make meaning of it. VPNs’ most common tunneling and encryption protocols are PPTP, L2TP/IPSec, IKEv2/IPSec, SSTP, and OpenVPN. These all have pros and cons, but we recommend OpenVPN based on its outstanding performance and strong encryption.
VPS vs VPN – Significant Differences
| VPS | VPN |
| Hosts your sites and applications. | Keeps your information private and secure and changes how your web traffic travels. |
| Widely used in businesses. | Individuals and businesses use it. |
| Hosted sites or applications can be vulnerable. | Mainly focused and designed around its security features. |
| Can’t change the apparent location of the web traffic. | It enables you to pass through geo-blocking. |
| Requires good knowledge of servers. | A very affordable method or service with anonymity for your web journey. |
Can I use a VPS as a VPN? (VPS vs VPN)
No. A VPN (Virtual Private Network) and a VPS (Virtual Private Server) are two different technologies. VPNs will secure your activities online by making you invisible, while VPS is a server you can rent to host your service.
However, these two technologies can be combined and used together. You can use a VPN to secure your virtual private server.