Table of Contents
VPS vs Cloud Server – There is a lot of talk these days about cloud computing or cloud hosting. Many companies are using these terms loosely to discuss either VPS or cloud servers (public or private). But, what do these terms mean? You will definitely see a difference when you look at the price tag, so understanding what each of these services are will help you in your quest to determine the best option for you or your company.
To help you out, here is a description of each and even some of their pros and cons
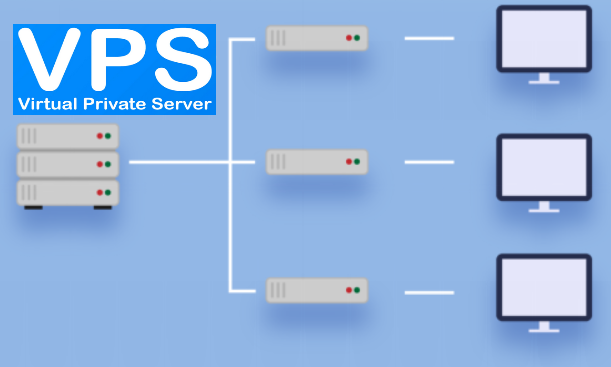
Virtual Private Server
Definition: One physical server, divided into several smaller server slices that each act as their own virtual server environment.
If shared hosting is like sharing a flat with noisy neighbours, then VPS is like living in a nice house with the ability to change furniture and fittings and even add extra rooms, and it’s all yours, no sharing.
Because VPS is an implementation of IAAS you get full virtual Servers with your choice of operating system i.e windows server or linux flavours. The servers usually come loaded with web app dev tools, databases and in some cases email servers as well. In most cases you get assigned an i.p address but you can optionally request for more, additionally because you are getting a full virual server with root access, you can remote in and install whatsoever you wish and host as many websites as you want.
Advantages of VPS Server
VPS hosting has been one of the most popular options for a long time. Look at the key benefits that make it so attractive:
- Exclusive access to resources: Your website is assigned a set amount of disk space, central processing unit (CPU) utilization, memory, and other resources so that other accounts won’t impact it on the same server.
- Ability to customize: Since you’re given full access to your virtual server, you can configure it in any way you want, which is generally impossible with shared hosting.
- Affordable: You get many of the same benefits associated with dedicated servers but at a fraction of the cost.
Who Should Use VPS Hosting?
A VPS can be a great choice for website users who have outgrown their shared hosting plan. However, it’s not perfect for every kind of website out there. Virtual Private Server hosting is great for users looking for more control over their website, with the technical skills to set up a customized environment.
Specifically, VPS may be right for you if:
- You’re planning a website that has complexity, and your programmer will want more power over customization.
- You have too much traffic for a shared web hosting plan to make sense, but your traffic numbers are typically consistent month to month, so you have a pretty good idea of how much bandwidth you’ll need.
- You have a specific type of software (or more than one) your website will require, and you expect to need direct access to the server to install and maintain it.
- You expect to run custom scripts and plugins on your site—the customization power VPS plans provide often work better for this.
Cloud Server
Definition: Cloud servers utilize multiple servers connected together in a cluster which is backed by SAN storage. Customers utilizing a cloud platform will benefit from the multiple servers because they will receive unlimited storage, maximum bandwidth, managed load balancing and no ties to a specific piece of hardware. The basic difference between public and private clouds are in public, the cluster is multi-tenant and a private is a single client.
Cloud hosting is when your hosting plan taps into a network of potentially unlimited virtual machines. All of these virtual machines rely upon an underlying network of connected physical servers. With all of these virtual machines connected together, cloud hosting functions somewhat like one big VPS.
Advantages of Cloud Hosting
- Because your website is hosted on a virtual partition that utilizes numerous physical networks, cloud hosting is relatively reliable. When one of the servers goes down, the cloud’s resource level drops significantly, but it has no effect on your website. There isn’t any inaccessibility or anything like that.
- Many physical servers defend cloud hosting against third-parties attempting to gain access to their facilities or disrupt their services.
- Cloud hosting is adaptable, scalable, and expandable. It is not constrained in the same way that a single server is. Resources are available in real time and in response to your demands.
- Because you only pay for what you use, cloud hosting is cost-effective.
Who Should Use Cloud Hosting?
Cloud hosting is a great choice for website owners who need the flexibility that the cloud provides to enable increased performance to meet surges in traffic.
Specifically, cloud hosting may be the best choice for you if:
- Your traffic numbers vary considerably month to month, such as with an eCommerce store with seasonal products or a media site with the occasional viral article.
- You anticipate a lot of growth in the coming years and want to choose a web hosting plan that can grow with you. New startups or companies implementing a growth strategy are likely to prefer cloud hosting.
- You like the idea of only paying for what you need. That can mean inconsistent billing month to month that’s harder to plan for, but it could result in overall savings for some websites.
VPS vs Cloud Server
VPS vs Cloud Server VPS vs Cloud Server VPS vs Cloud Server VPS vs Cloud Server VPS vs Cloud Server VPS vs Cloud Server VPS vs Cloud Server VPS vs Cloud Server VPS vs Cloud Server